(1) Proportional measurements:
- The body parts are divided into definite proportional equal units (Cun, a measurement unit in Chinese) for locating points, regardless of the person’s gender, age, and body size.
- It was called Gu Du Fa (
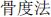 , Bone measurement Method) in ancient times and first recorded in, “Gu Du,” of The Miraculous Pivot.
, Bone measurement Method) in ancient times and first recorded in, “Gu Du,” of The Miraculous Pivot.
(2) Anatomical landmarks:
- Fixed landmarks: sense organs, hairline, eyebrows, nails, umbilicus, prominence or depression/groove of bones.
- Moving landmarks: skin creases, muscle bulge or depression, aperture of joints, etc.
(3) Finger-length measurements:
| (a) | Middle finger measurement. |
| (b) | Thumb measurement. |
| (c) | Four-finger measurement: Yi Fu Fa 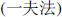 . . |
(4)Simple, fast methods: based on experience, such as locating LU 7, GB 31, or LR 13.
(5)Considerations:
| (a) | The above-mentioned methods should be used comprehensively, to ensure accuracy of a point location. |
| (b) | Choose the most applicable method. |
| (c) | As a practitioner, you must compensate for the difference of measurement between your own finger length and your patient’s. |

