The Introduction of Insomnia
Definition
This is a disease in which the amount and quality of sleep are decreased constantly. It is called Bu Mai (“no sleep”) or Shi Mian (“loss of sleep”) in TCM.
Clinical features
- Difficulty in falling asleep.
- Waking up easily during the night.
- Waking up early in the morning.
- Dream-disturbed sleep.
- Inability to sleep through the night.
Corresponding diseases in CWM
- Neurosis
- Menopause
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Drug withdrawal effects
- Direct drug side effects
- Painful diseases
- Asthma
Sometimes insomnia is the primary cause, while at other times it is a secondary cause. If it is a secondary cause, then you must treat the primary disease first to relieve the insomnia.
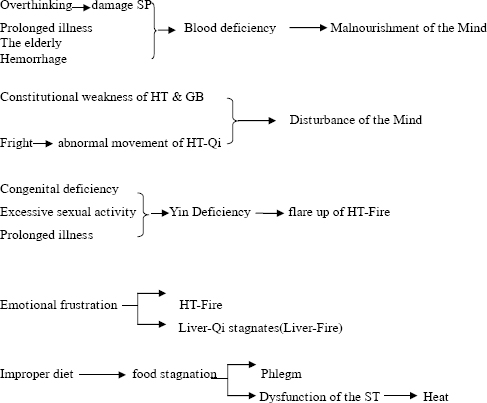
The Etiology of Insomnia
(See picture Etiology of insomnia)
The pathology of Insomnia
The chief pathology of insomnia is either excess or deficiency. Excess is due to disturbance of the Mind, while deficiency is due to malnourishment of the Mind. The chief organ involved is the Heart. The Heart fails to properly house the Mind. Insomnia is also associated with the Liver, Gall Bladder, Spleen, Stomach, and Kidney.
Disturbance of the mind by heat
Heat mainly comes from:
- Another organ close to the Heart (or the Heart itself) disturbs the Heart and Shen.
- Warm Disease progresses from the Wei to the Qi to the Ying to the Blood level. When Heat moves to the Ying or Blood level, it will disturb the Mind, leading to insomnia.
The main symptoms of Heat disturbing the Mind:
- Difficulty in falling asleep. (At night Yang is meant to enter the Yin level, merging with Yin, to result in sleep. Then Yin governs the body. In the morning, Yang re-emerges from Yin, causing the person to wake up.)
- Restlessness.
- A feverish sensation in the Heart, dream-disturbed sleep, and palpitations may also be present.
Malnourishment of Shen
The spirit and Qi belong to Yang. They need Yin and Blood to nourish them (especially Heart-Yin and Heart-Blood). Blood is the source of Shen: without Blood the Spirit will go away — the invisible, must attach to the visible body.
Heart-Blood deficiency or Heart-Yin deficiency failing to nourish Shen leads to insomnia:
- Early awakening.
- Difficulty in returning to sleep.
- May have difficulty in falling asleep (no restlessness symptoms, because generally there is no heat associated with this pattern).
Deficiency of Shen
Not enough Spirit. The Gall Bladder dominates courage, and this type of condition is usually associated with Heart or Gall bladder Qi deficiency leading to Shen deficiency.
Heart-Qi or Gall Bladder-Qi deficiency:
- Lack of energy.
- Palpitations.
- Timid personality, being easily frightened.
- Waking several times during the night.
- Often having nightmares and disturbing dreams.
How to Diagnose and differentiate Insomnia
(see Table 26)
Diagnosis
It is not difficult to diagnose insomnia based on its clinical features. Both sleep time and sleep quality are important. Primary and secondary insomnia have to be identified. Primary insomnia is sleeplessness that is not attributable to a medical, psychiatric, or environmental cause. The etiology of primary insomnia relates in part to psychological conditioning processes. Secondary insomnia is a symptom caused by medical, psychiatric, or environmental factors.
Syndrome differentiation tips
(1)Determine the organ involved
- Hot temper, insomnia → Liver-Fire affecting the Heart.
- Epigastric fullness, greasy tongue, insomnia → food retention in the Stomach leading to Phlegm.
- Insomnia and restlessness, palpitations, dizziness, poor memory → deficiency Fire flaring up.
- Insomnia and sallow complexion, fatigue, listlessness → Spleen deficiency plus Heart-Blood deficiency.
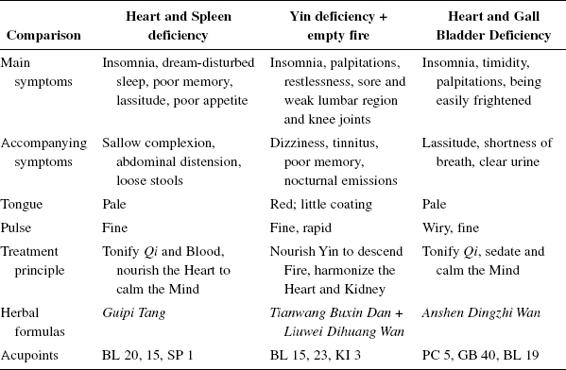
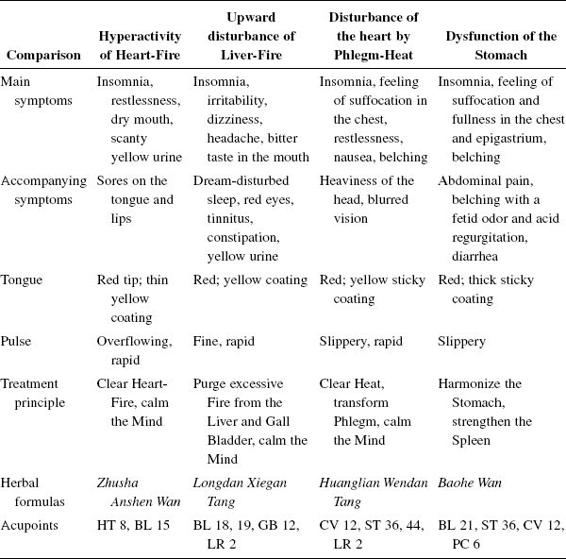
Basic points: HT 7, SP 6, Anmian.
(2)Differentiate between excess and deficiency
Deficiency (usually Yin/Blood deficiency failing to nourish the Heart):
- Thin person
- Sallow complexion
- Listlessness
- Fatigue
- Reluctance to speak
- Palpitations
- Poor memory (Spleen deficiency, the Liver failing to store Blood, the Kidney failing to store Essence)
Excess (usually caused by Heat disturbing the Heart):
- Restlessness
- Anger
- Bitter taste in the mouth
- Dry throat
- Constipation
- Dark-yellow urine (Heart-Fire or Liver-Fire)
The Treatment of Insomnia
Principle of treatment
- Calm the Mind as a universal treatment principle.
- For excess patterns, reduce excess through soothing the Liver and regulating Qi; clearing Fire, removing Phlegm, or promoting digestion.
- For deficiency patterns, tonify deficiency through tonifying Qi, nourishing Blood, strengthening the Spleen, and tonifying the Liver and Kidney.
- For the combined pattern, include both reducing and tonifying.
Herbals
See the Differentiation and Treatment Table 26.
Acupuncture
(1)Primary meridians for treating insomnia
- Heart and Pericardium Meridians.
- Liver, Spleen, and Kidney Meridians.
(2)Primary points
- HT 7 — Yuan source point of the Heart to calm the Mind and nourish the Heart.
- SP6 — crossing point of three Foot Yin meridians to regulate Liver, Spleen, and Kidney Meridians and nourish Qi and Blood.
- Anmian — calms the Mind.
- Sishencong — calms the Mind.
(3)Point selection based on the pattern
See Table 26.
Auricular acupuncture
- Subcortex
- Sympathetic
- Heart
- Spleen
- Kidney
- Endocrine
- Shenmen
Two or three points each time; needles or ear seeds.
Moxa
- Moxa GV 20 for 10–15 min before bed every night.
Plum blossom needle
- Light tapping around the neck and upper back. Focus on the GV Meridian and BL Meridian.
Suggestions
- Insomnia is a psychological disorder, so counseling the patient is very important.
- Regular exercise, especially for people who use their minds a lot.
- Do not drink concentrated tea, coffee, or alcohol or smoke cigarettes before bed.
- Cultivate good life habits, such as going to bed around the same time every day to encourage a conditioned response in the body.
- Light tapping around the neck and upper back. Focus on the GV Meridian and BL Meridian.
Suggestions
- Insomnia is a psychological disorder, so counseling the patient is very important.
- Regular exercise, especially for people who use their minds a lot.
- Do not drink concentrated tea, coffee, or alcohol or smoke cigarettes before bed.
- Cultivate good life habits, such as going to bed around the same time every day to encourage a conditioned response in the body.

