- Sì Shén Cōng (EX-HN 1, 四神聪)
- Dāng Yáng (EX-HN 2, 当阳)
- Yìn Táng (EX-HN 3, 印堂)
- Yú Yāo (EX-HN 4, 鱼腰)
- Tài Yáng (EX-HN 5, 太阳)
- Ěr Jiān (EX-HN 6, 耳尖)
- Qiú Hòu (EX-HN 7, 球后)
- Shàng Yíng Xiāng (EX-HN 8, 上迎香)
- Nèi Yíng Xiāng (EX-HN 9, 内迎香)
- Jù Quán (EX-HN 10, 聚泉)
- Hǎi Quán (EX-HN 11, 海泉)
- Jīn Jīn (EX-HN 12, 金津)
- Yù Yè (EX-HN 13, 玉液)
- Yì Míng (EX-HN 14, 翳明)
- Jǐng Bǎi Láo (EX-HN 15, 颈百劳)
Sì Shén Cōng (EX-HN 1, 四神聪)
Location. At the vertex of the scalp; four points, 1 cun respectively anterior, posterior, and lateral to DU 20 (băihuì) (Pic. 3-105).
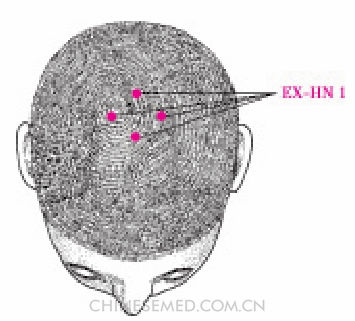
Location.method. Find DU 20, where the midline of the head intersects a line connecting the ear apexes. The four points are located respectively 1 cun anterior, posterior, and lateral to that point.
Actions. Tranquilize and calm the mind, clear the head and eyes, and open the orifices.
Indications. Headache, vertigo, insomnia, forgetfulness, epilepsy, hydrocephalus, cerebral agenesis. Headache, insomnia, and vertigo can be prevented by massaging and pressing sì shén cōng (EX-HN 1) 5~10 minutes a day.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: Needle transversely 0.5~0.8 cun toward DU 20 or the periphery to cause local soreness and distention. Moxibustion: Use 1~3 cones of cone moxibustion or 5~8 minutes with a moxa stick.
Dāng Yáng (EX-HN 2, 当阳)
Location. On the head directly above the pupil, 1 cun superior to the anterior hairline (Pic. 3-106).
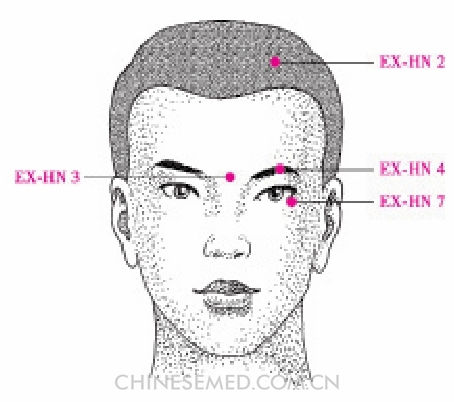
Location.method. The point is 0.5 cun directly above GB 15 (tóu lín qì) at the level of DU 23 (shàng xīng).
Actions. Improve vision, induce resuscitation, scatter wind, and dredge collaterals.
Indications. Headache, vertigo, insomnia, forgetfulness, epilepsy.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: Needle transversely upward or downward 0.3~0.5 cun to produce local heaviness and distention. Moxibustion: Use 1~3 cones of cone moxibustion or 3~5 minutes with a moxa stick.
Yìn Táng (EX-HN 3, 印堂)
Location. At the midpoint between the medial ends of the eyebrows (Pic. 3-106).
Indications. Headache, vertigo, insomnia, forgetfulness, epilepsy, infantile convulsion, nosebleed, sinusitis.
Manipulation. Needle transversely 0.3~0.5 cun or prick to induce bleeding.
Yú Yāo (EX-HN 4, 鱼腰)
Location. At the center of the eyebrow in the depression directly above the pupil when the eyes are looking straight ahead (Pic. 3-106).
Actions. Clear liver heat and improve vision, unblock collaterals and relieve pain.
Indications. Twitching of the eyelids, deviation of mouth and eye, ptosis of the eyelids, red and painful eyes, trigeminal neuralgia.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: 1. Needle transversely 0.5~1.0 cun toward BL 2 (cuán zhú) or SJ 23 (sī zhú kōng) to produce local heaviness and distention that radiates to the eyeball. 2. For trigeminal neuralgia, needle obliquely 0.3~0.5 cun toward the anteroinferior aspect to reach the supraorbital foramen until an electric shock radiates to the eye and forehead to treat. Moxibustion is forbidden.
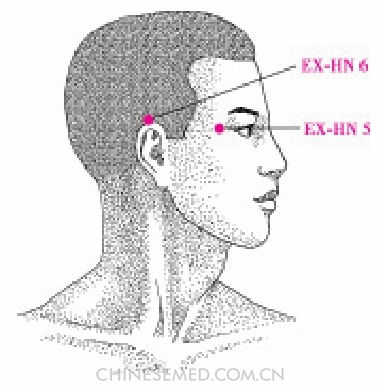
Tài Yáng (EX-HN 5, 太阳)
Location. At the temple in the depression about one fnger-breadth posterior to the midpoint of the lateral end of the eyebrow and the outer canthus (Pic. 3-107).
Location.method. The point is about a fnger-breadth lateral to the midpoint of a line connecting SJ 23 (sī zhú kōng) and GB 1 (tóng zĭ liáo).
Actions. Clear heat, dispel wind, arrest convulsions, and relieve pain.
Indications. Mental disorders such as headache, vertigo, insomnia, forgetfulness, epilepsy; eye disorders.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: 1. Needle perpendicularly 0.3~0.5 cun to cause local soreness and distention. 2. For migraine, penetrate GB 8 (shuài gŭ) by needling transversely 1.0~2.0 cun backward to induce local soreness and distention that radiates to the ipsilateral temporal region. 3. For facial paralysis, penetrate ST 7 (xià guān) by needling transversely 1.5~2.5 cun downward to cause local soreness and distention that radiates to the cheek. 4. Prick to bleed with a three-edged needle. Moxibustion: 3~5 cones of cone moxibustion or 20 minutes of warming needle moxibustion, or 5~10 minutes with a moxa stick, or use medicinal and natural moxibustion.
Ěr Jiān (EX-HN 6, 耳尖)
Location. At the highest point of the external ear auricle (Pic. 3-107).
Location.method. With the ear folded forward, the point is at the apex of the ear.
Actions. Drain heat and cool blood, improve vision and relieve pain.
Indications. Eye disorders such as acute conjunctivitis, hordeolum, trachoma; headache; swelling and pain in the throat; hyperpyrexia.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: 1. Needle perpendicularly 0.1~0.2 cun to produce local soreness and distention. 2. Prick with a three-edged needle and press to bleed. Moxibustion: 3~5 cones of cone moxibustion or 5~10 minutes with a moxa stick.
Qiú Hòu (EX-HN 7, 球后)
Location. On the face at the junction of the lateral 1/4 and medial 3/4 of the infraorbital margin (Pic. 3-106).
1 Wang RC, Huang YH, Pan WJ, Xu XE. One hundred and eighty cases of hordeolum treated by point bleeding after massaging tài yán⁝ (EX-HN 5) and ĕr jiān (EX-HN 6) 太阳、耳尖穴按摩后放血治疗麦粒肿180例. Zhejiang Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2008; 43(6): 360.
Location.method. The point is on the infraorbital margin at the junction of the lateral 1/4 and medial 3/4 of a line drawn between the inner and outer canthi.
Actions. Clear heat and improve vision.
Indications. Optic neuritis, optic atrophy, retinal pigment degeneration, vitreous opacity, glaucoma, esotropia, iridocyclitis.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: Use the left hand to push the eyeball upward; with the right hand, slowly needle upward 0.5~1.5 cun medially toward the optic nerve to cause soreness, distention, and a bulging sensation in the eyeball. Do not lift, thrust, twirl, or insert the needle too deeply. Moxibustion is forbidden.
Precautions. 1. The needle should not touch the eyeball. Push the eyeball slightly with the fnger, and insert the needle along the infraorbital margin. 2. Avoid puncturing the veins in the orbit. Insert slowly without lifting, thrusting, or twirling. 3. Do not puncture the nerves or enter the cranial cavity by needling too deeply.
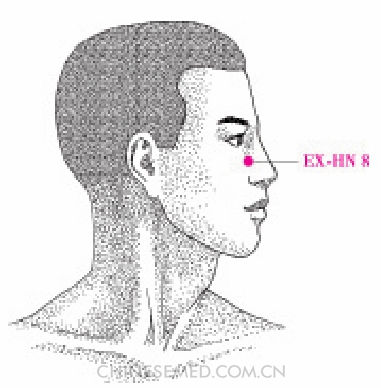
Shàng Yíng Xiāng (EX-HN 8, 上迎香)
Location. On the face at the junction of the cartilage of the ala nasi and the nasal concha, near the upper end of the nasolabial groove (Pic. 3-108).
Actions. Clear heat and open the orifices, unblock collaterals and relieve pain.
Indications. Allergic rhinitis, atrophic rhinitis, furuncle of nose, sinusitis, nosebleed, lower olfactory dysfunction.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: Needle obliquely 0.5~ 0.8 cun upward and medially to cause local soreness and distention that radiates to the nasofrontal region and eyeball. Moxibustion: Use a moxa stick for 5~10 minutes.
Nèi Yíng Xiāng (EX-HN 9, 内迎香)
Location. Inside the nostrils on the mucosal membrane at the junction of the cartilage of the ala nasi and the nasal concha (Pic. 3-109).
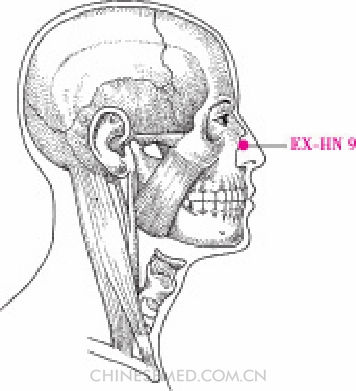
Location.method. The point is on the mucosal membrane opposite shàng yíng xiāng (EX-HN 8).
Actions. Clear heat and disperse wind, diffuse and unblock the nasal orifices.
Indications. Headache, vertigo, severe convulsion; fve sensory organ disorders including swelling and pain in the eyes, rhinitis, and pharyngitis; heatstroke.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: 1. Needle perpendicularly and medially 0.1~0.2 cun from the nostrils. 2. Bleed 1~2 ml with a three-edged needle. This method is forbidden in bleeding disorders or hypertension. Moxibustion is forbidden.
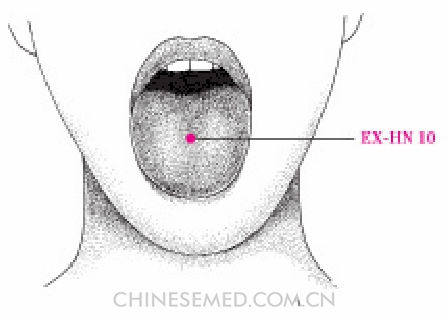
Jù Quán (EX-HN 10, 聚泉)
Location. In the mouth cavity at the midpoint of the center line of the tongue (Pic. 3-110).
Actions. Clear heat, disperse wind, dispel pathogens, and open the orifices.
Indications. Cough, asthma, aphasia after cerebrovascular events.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: 1. Needle perpendicularly 0.1~0.2 cun, soreness and distention can be felt locally or throughout the tongue. 2. Bleed with a three-edged needle.
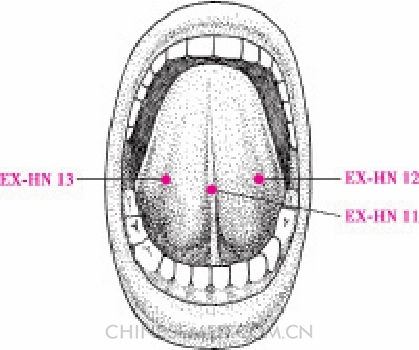
Hǎi Quán (EX-HN 11, 海泉)
Location. In the mouth at the midpoint of the lingual frenulum (Pic. 3-111).
Actions. Dispel pathogens, open the orifices, and stimulate fuids to quench thirst.
Indications. Aphtha, sore tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hyperpyrexia, unconsciousness, pharyngitis, aphasia after cerebrovascular events, diabetes.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: 1. Insert perpendicularly 0.1~0.2 cun to cause soreness and distention locally or throughout the tongue. 2. Bleed with a three-edged needle. Moxibustion: Moxibustion is not usually used.
Jīn Jīn (EX-HN 12, 金津)
Location. In the mouth on the left vein of the lingual frenulum (Pic. 3-111).
Actions. Clear heat and resolve toxins, dispel pathogens, and open the orifices.
Indications. Stomatitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis; aphasia after cerebrovascular events, vomiting, diarrhea.
Manipulation. Bleed with a three-edged needle.
Yù Yè (EX-HN 13, 玉液)
Location. In the mouth on the right vein of the lingual frenulum (Pic. 3-111). Actions. Clear heat, resolve toxins, dispel pathogens, and open the orifices. Indications. Stomatitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis; aphasia after cerebrovascular events, vomiting, diarrhea.
Manipulation. Bleed with a three-edged needle.
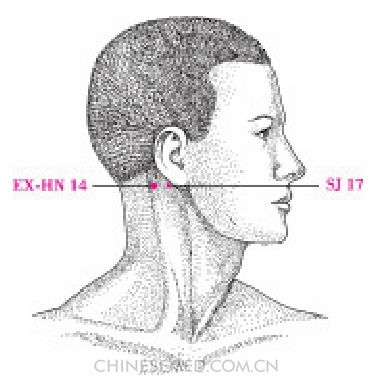
Yì Míng (EX-HN 14, 翳明)
Location. On the neck 1 cun posterior to SJ 17 (yìfēng) (Pic. 3-112).
Actions. Improve vision and hearing, tranquilize and calm the mind.
Indications. Hyperopia, myopia, nyctalopia, cataract, glaucoma, optic atrophy, tinnitus; headache, vertigo, insomnia.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: Needle perpendicularly 0.5~1.5 cun to cause local soreness and distention that radiates to the head. Moxibustion: Use 3~5 cones of cone moxibustion or 20 minutes of warming needle moxibustion or 5~10 minutes with a moxa stick.
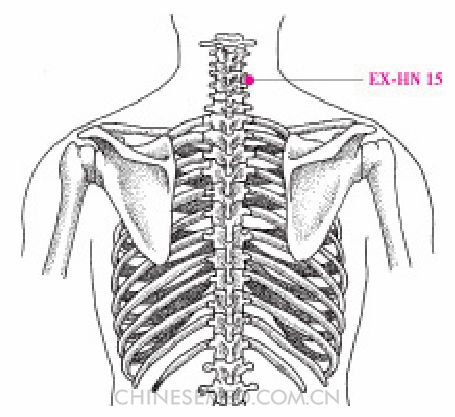
Jǐng Bǎi Láo (EX-HN 15, 颈百劳)
Location. On the neck 2 cun directly superior to the seventh cervical spinous process and 1 cun lateral to the posterior midline (Pic. 3-113).
Location.method. The point is 2 cun above and 1 cun lateral to DU 14 (dà zhuī).
Actions. Nourish yin and reinforce the lung, relax sinews and unblock collaterals.
Indications. Bronchitis, bronchial asthma, and phthisis; cervical spondylosis.
Manipulation. Acupuncture: 1. Insert perpendicularly 0.5~1.0 cun. 2. Needle obliquely 0.5~1.0 cun to cause local soreness and distention. Moxibustion: Use 5~9 cones of cone moxibustion or use warming needle moxibustion for 20 minutes, or 10~20 minutes with a moxa stick; medicinal and natural moxibustion may be used.
Precautions. Deep insertion forward and medially in this region might pierce the ligament, enter the spinal canal, and damage the spinal cord.

