The 18 incompatible herbs (shibafan 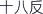 ) and 19 herbs of mutual antagonism (shijiuwei
) and 19 herbs of mutual antagonism (shijiuwei 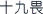 ) are specific taboo medicines ofpeiwu
) are specific taboo medicines ofpeiwu 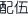 . The three main taboos to be avoided when using Chinese medicines are herbal incompatibility (peiwu jinji
. The three main taboos to be avoided when using Chinese medicines are herbal incompatibility (peiwu jinji  ), taboo food (yinshi jinji
), taboo food (yinshi jinji  ) and taboo during pregnancy (yunfu jinji
) and taboo during pregnancy (yunfu jinji  ).
).
Herbal incompatibility
Compatibility of medicines (peiwu 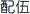 ) refers to the combined usage of two or more medicinal materials based on the symptoms of the ailment and the medicines’ nature. Herbal incompatibility
) refers to the combined usage of two or more medicinal materials based on the symptoms of the ailment and the medicines’ nature. Herbal incompatibility  refers to the toxic side effects produced when certain medicines are used in combination, or when the combination causes the original curative effects of the medicines to be reduced or reversed.
refers to the toxic side effects produced when certain medicines are used in combination, or when the combination causes the original curative effects of the medicines to be reduced or reversed.
Herbal Incompatibility

Taboo food
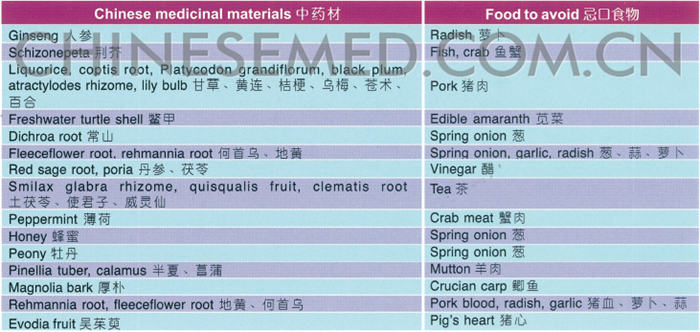
When one falls ill or takes medication, the consumption of certain food will reduce the medicine’s original curative effects, or aggravate the patient’s condition, or lead to the development of other illnesses. Hence, such food, also known as taboo food, should be avoided when we are on Chinese medication.
Different taboo foods should be avoided depending on the illness. E.g. patients with liver disease should avoid spicy food; patients with heart disease should avoid salty food; patients with edema should avoid salt; patients with bone disease should avoid the combination of sour and sweet; patients with gall bladder disease should avoid oily food; patients with cold illnesses should avoid melon; and patients with sores should avoid fish and prawns.

Foods to avoid while on the following Chinese medications:
Taboo during pregnancy
This refers to medicinal herbs which bring about harmful effects to a pregnant woman and her foetus. They may affect the normal gestation process, resulting in vaginal bleeding during pregnancy, continuous movement of the foetus causing lower abdominal pain, abortion, miscarriage or death of foetus in womb, deformity of foetus, etc. Based on the degree of toxicity and side effects, Chinese medicines for pregnant women are classified under forbidden medicines (jinyongyao  ) and medicines to be used with caution (shenyongya
) and medicines to be used with caution (shenyongya  ).
).
Forbidden medicines : refers to medicines with high levels of toxicity and strong effects, causing great harm to both the mother and foetus, resulting in abortion or the death of foetus. E.g. mercury, white arsenic, croton seed, knoxia root, pokeberry root, false hellebore root and rhizome, Sichuan aconite root, realgar, blue vitriol, melon pedicle, musk, pharbitis seed, zedoary, leech, etc.
Medicines to be used with caution : refers to medicines with lower level of toxicity, having milder effects. E.g. achyranthes root, chuanxiong rhizome, safflower, peach kernel, turmeria, moutan bark, immature orange fruit, senna leaf, aloes, mirabilite, prepared aconite branch-root, cinnamon bark, betel nut, green tangerine peel, rhubarb, water-plantain tuber, oyster shell, flavescent sophora root, asarum herb, etc.

Chinese medicines with varying harmful effects on pregnant women and foetus


